与AOV网对应的,还有一个AOE网,当然它也是有DAG(向无环图)。
AOE(Activity On Edge)网:顾名思义,用边表示活动的网。
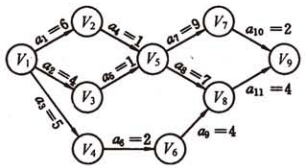
与AOV不同,活动都表示在了边上,如下图所示:
如上所示,共有11项活动(11条边),9个事件(9个顶点)。
整个工程只有一个开始点和一个完成点。
即只有一个入度为零的点(源点)和只有一个出度为零的点(汇点)。
(1) 关键路径:是从开始点到完成点的最长路径的长度。路径的长度是边上活动耗费的时间。
(2) 最早发生时间:v1到vi的最长路径叫做vi的最早发生时间,用ei表示。例如上图中,v5的最早发生时间是max(6+1, 4+1) = 7。
(3) 最迟开始时间:在不推迟整个工程完成的前提下,活动i最迟必须开始进行的时间,用l(i)表示。l(i) - e(i)是活动的时间余量。
(4) 关键活动:l(i)=e(i)的活动称为关键活动。
关键路径上的活动都是关键活动。
提前完成非关键活动并不能加快工程进度(类似木桶效应)。
AOE网的主要活动就是识别出哪些是关键活动,以便争取提高关键活动的工效,缩短整个工期。
当然,如果AOE网发生了改变,那么原先的关键路径也会发生变化。
因此,只有在不改变挂件路径的情况下,提供关键活动的速度,才能对整体工程进度起到帮助作用。
求关键路径的算法
求关键路径,就是要求e(i) = l(i)的事件(点)。我们首先必须分别求出所有点的e(i)和l(i)。
由于ve和vl的递推公式必须在拓扑排序下有效,因此,先要求拓扑排序
0、求拓扑排序(同时顺道求ve)
要增设一个栈T记录拓扑有序序列,计算求得各个顶点的ve之后,从栈顶依次弹出栈,就可以倒序遍历,求vl了。
还要使用拓扑排序的那个入度为0的栈,可以每次Pop时候顺道记录下,最后cnt如果<g->nvexs,则表示有环。
1、求最早发生时间ve[]
ve(0)=0开始递推
ve(j) = max{ve{i}+dut(i, j)}
2、求最晚发生时间vl[]
从vl(n-1)=ve(n-1)开始倒推。
vl(j) = min{vl(i) - dut(j, i)}。
3、遍历,求出ve(i) = vl(i)的所有点i。
算法总时间复杂度是O(n+e)。
具体的代码如下:
求拓扑排序和ve、以及栈T
void topo_sort_ve(struct Graph* g, struct Stack* tstk, int* ve)
{
// Malloc
int* indeg = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*g->nvexs);
int i = 0;
int j;
int cnt = 0;
struct Arc* ptr = NULL;
struct Stack* stk = (struct Stack*)malloc(sizeof(struct Stack));
// Init stk
stack_init(stk);
// Compute indegree
memset(indeg, 0, sizeof(int)*g->nvexs);
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
ptr = g->vexs[i].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
indeg[ptr->ivex]++;
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
// Push all vex that indeg is 0
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
if(indeg[i]==0)
{
if(-1==stack_push(stk, i))
{
printf("Stack push fail.\n");
return ;
}
}
}
// while ! stk.empty
memset(ve, 0, sizeof(int)*g->nvexs);
while(!stack_is_empty(stk))
{
// Pop
if(-1==stack_pop(stk, &j))
{
printf("Stack pop fail.\n");
return ;
}
// Topo stk
if(-1==stack_push(tstk, j))
{
printf("Stack push fail.\n");
return ;
}
// Cnt
cnt++;
// Process all neghbour
ptr = g->vexs[j].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
// Push if indegree change to zero
if(--indeg[ptr->ivex]==0)
{
stack_push(stk, ptr->ivex);
}
// ve[k] = max(e(j) arc(j, k))
if(ve[j] + ptr->w > ve[ptr->ivex])
{
ve[ptr->ivex] = ve[j] + ptr->w;
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
// Free
free(indeg);
free(stk);
// Cnt to see if has cycle
if(cnt<g->nvexs)
{
printf("Has Cycle!\n");
}
return ;
}
求vl
void topo_vl(struct Graph* g, struct Stack* tstk, int* ve, int* vl)
{
int i;
int j;
struct Arc* ptr = NULL;
// Pop end point
if(-1==stack_pop(tstk, &j))
{
printf("Pop fail.\n");
return ;
}
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
vl[i] = ve[j];
}
// while ! empty
while(!stack_is_empty(tstk))
{
// Pop j
if(-1==stack_pop(tstk, &j))
{
printf("Pop fail.\n");
return ;
}
// vl[j] = min(vl[k]-arc(j,k)), k is ptr->ivex
ptr = g->vexs[j].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
if(vl[ptr->ivex] - ptr->w < vl[j])
{
vl[j] = vl[ptr->ivex] - ptr->w;
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
return ;
}
求关键路径
void critical_path(struct Graph* g, int* ve, int* vl)
{
int i;
printf("Critical Path:");
for(i=0;i<g->nvexs;i++)
{
if(ve[i]==vl[i])
{
printf("%d ", g->vexs[i].data);
}
}
printf("\n");
}
其他代码,如创建等,注意我们要存储活动的耗费,给Arc加了一个权值w。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_VEXS 100
#define MAX_QUEUE 1000
// Arc
struct Arc
{
int ivex; // The vex position in vexs array
int w; // The data on arc(path)
struct Arc* next;
};
// Vex
struct Vex
{
int data;
struct Arc* first_arc;
};
// Graph
struct Graph
{
struct Vex vexs[MAX_VEXS];
int nvexs;
int narcs;
};
int graph_locate(struct Graph* g, int val)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
if(g->vexs[i].data==val)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void graph_add_arc(struct Graph* g, int x, int y, int w)
{
// New arc
struct Arc* new_arc = (struct Arc*)malloc(sizeof(struct Arc));
struct Arc* ptr = NULL;
if(!new_arc)
{
return ;
}
new_arc->ivex = y;
new_arc->w = w;
new_arc->next = NULL;
// Find vexs[x]'s tail
if(!g->vexs[x].first_arc)
{
g->vexs[x].first_arc = new_arc;
}else
{
ptr = g->vexs[x].first_arc;
while(ptr->next!=NULL)
{
ptr = ptr->next;
}
ptr->next = new_arc;
}
}
void graph_create(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
int x, y, w;
struct Arc* ptr;
// Get n vexs
printf("Please enter n for number of vexs:\n");
scanf("%d", &g->nvexs);
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
printf("Please enter a int for vexs(%d):\n", i);
scanf("%d", &g->vexs[i].data);
g->vexs[i].first_arc = NULL;
}
// Get m arcs;
printf("Please enter m for number of vexs:\n");
scanf("%d", &g->narcs);
for(i=0; i<g->narcs; i++)
{
printf("Please enter x y w for arcs(%d):\n", i);
scanf("%d %d %d", &x, &y, &w);
x = graph_locate(g, x);
y = graph_locate(g, y);
if(x==-1 || y==-1)
{
printf("Wrong x or y for arcs(%d).\n", i);
i--;
}
// arc x->y
graph_add_arc(g, x, y, w);
}
}
void graph_print(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
struct Arc* ptr;
// Just print arcs
for(i=0;i<g->nvexs;i++)
{
ptr = g->vexs[i].first_arc;
while(ptr)
{
printf("%d->%d\n", g->vexs[i].data, g->vexs[ptr->ivex].data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
void graph_init(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<MAX_VEXS; i++)
{
g->vexs[i].first_arc = NULL;
}
g->nvexs = 0;
g->narcs = 0;
}
void graph_free(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
struct Arc* ptr;
struct Arc* free_node;
g->nvexs = 0;
g->narcs = 0;
for(i=0; i<MAX_VEXS; i++)
{
ptr = g->vexs[i].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
free_node = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
free(free_node);
}
}
}
#define MAX_STACK 100
struct Stack
{
int top;
int data[MAX_STACK];
};
void stack_init(struct Stack* stk)
{
stk->top = 0;
}
int stack_push(struct Stack* stk, int v)
{
if(stk->top>=MAX_STACK)
{
return -1;
}else
{
stk->data[stk->top++] = v;
return 0;
}
}
int stack_pop(struct Stack* stk, int* v)
{
if(stk->top==0)
{
return -1;
}else
{
*v = stk->data[--stk->top];
return 0;
}
}
int stack_is_empty(struct Stack* stk)
{
return stk->top==0;
}
测试驱动:
int main()
{
struct Graph g;
struct Stack tstk;
int ve[MAX_VEXS];
int vl[MAX_VEXS];
int i;
graph_init(&g);
graph_create(&g);
stack_init(&tstk);
topo_sort_ve(&g, &tstk, ve);
//for(i=0;i<g.nvexs;i++)
//{
// printf("%d\n", ve[i]);
//}
topo_vl(&g, &tstk, ve, vl);
//for(i=0;i<g.nvexs;i++)
//{
// printf("%d\n", vl[i]);
//}
critical_path(&g, ve, vl);
graph_free(&g);
return 0;
}
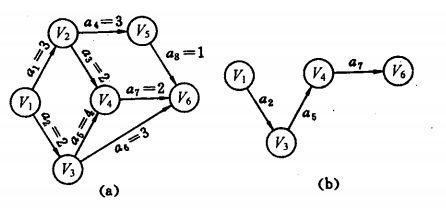
测试AOE图:
测试数据:
6 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 1 2 3 1 3 2 2 4 2 3 4 4 2 5 3 5 6 1 4 6 2 3 6 3
测试输出:
Critical Path:1 3 4 6