前面实现的邻接矩阵面临一个巨大的问题:对于稀疏矩阵,将耗费巨大的资源,而大部分都是0。
现实中,绝大多数矩阵都是稀疏的!
我们可以采用如下的邻接表方法存储。
首先定义每个弧如下:
ivex是在顶点在数组中的下标。
next是一条链表,即某个顶点i的所有邻接结点的弧组成。
// Arc
struct Arc
{
int ivex; // The vex position in vexs array
struct Arc* next;
};
然后对于每个顶点,定义如下:
// Vex
struct Vex
{
int data;
struct Arc* first_arc;
};
因此,图可以如下表示:
// Graph
struct Graph
{
struct Vex vexs[MAX_VEXS];
int nvexs;
int narcs;
};
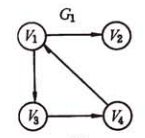
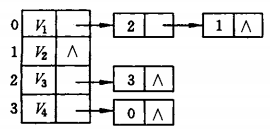
以书上的这个图为例:
实际上用邻接表存储是如下效果:
邻接表上很容易找到任意一个顶点的第一个邻接点和下一个。这对于dfs、bfs等遍历很有优势。
但是要判定任意两个顶点vi和vj是否有边或者弧,必须搜索第i个和/或第j个链表,不如邻接矩阵方便。
BFS算法
BFS(Breadth First Search),又叫广度优先搜索。使得“先被访问的顶点的邻接点”限于“后被访问的顶点的邻接点”。
其实就是类似于树中的层次遍历,也是借助队列实现。
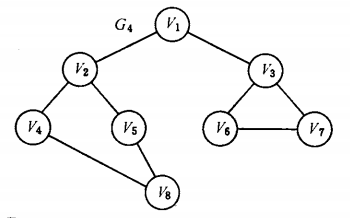
例如如下的图:
先访问v1,然后是v1的邻接点v2和v3,然后是v2的邻接点v4, v5,然后v3的邻接点。。。
最终次序:v1 -> v2 -> v3 -> v4 -> v5 -> v6 -> v7 -> v8
伪代码如下:
最终,使用循环队列+邻接表存储+BFS的代码如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_VEXS 100
#define MAX_QUEUE 1000
// Arc
struct Arc
{
int ivex; // The vex position in vexs array
struct Arc* next;
};
// Vex
struct Vex
{
int data;
struct Arc* first_arc;
};
// Graph
struct Graph
{
struct Vex vexs[MAX_VEXS];
int nvexs;
int narcs;
};
int graph_locate(struct Graph* g, int val)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
if(g->vexs[i].data==val)
{
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void graph_add_arc(struct Graph* g, int x, int y)
{
// New arc
struct Arc* new_arc = (struct Arc*)malloc(sizeof(struct Arc));
struct Arc* ptr = NULL;
if(!new_arc)
{
return ;
}
new_arc->ivex = y;
new_arc->next = NULL;
// Find vexs[x]'s tail
if(!g->vexs[x].first_arc)
{
g->vexs[x].first_arc = new_arc;
}else
{
ptr = g->vexs[x].first_arc;
while(ptr->next!=NULL)
{
ptr = ptr->next;
}
ptr->next = new_arc;
}
}
void graph_create(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
int x, y;
struct Arc* ptr;
// Get n vexs
printf("Please enter n for number of vexs:\n");
scanf("%d", &g->nvexs);
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
printf("Please enter a int for vexs(%d):\n", i);
scanf("%d", &g->vexs[i].data);
g->vexs[i].first_arc = NULL;
}
// Get m arcs;
printf("Please enter m for number of vexs:\n");
scanf("%d", &g->narcs);
for(i=0; i<g->narcs; i++)
{
printf("Please enter x y for arcs(%d):\n", i);
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
x = graph_locate(g, x);
y = graph_locate(g, y);
if(x==-1 || y==-1)
{
printf("Wrong x or y for arcs(%d).\n", i);
i--;
}
// arc x->y
graph_add_arc(g, x, y);
// arc y->x
graph_add_arc(g, y, x);
}
}
void graph_print(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
struct Arc* ptr;
// Just print arcs
for(i=0;i<g->nvexs;i++)
{
ptr = g->vexs[i].first_arc;
while(ptr)
{
printf("%d->%d\n", g->vexs[i].data, g->vexs[ptr->ivex].data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
void graph_init(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
for(i=0; i<MAX_VEXS; i++)
{
g->vexs[i].first_arc = NULL;
}
g->nvexs = 0;
g->narcs = 0;
}
void graph_free(struct Graph* g)
{
int i;
struct Arc* ptr;
struct Arc* free_node;
g->nvexs = 0;
g->narcs = 0;
for(i=0; i<MAX_VEXS; i++)
{
ptr = g->vexs[i].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
free_node = ptr;
ptr = ptr->next;
free(free_node);
}
}
}
struct Queue
{
int data[MAX_QUEUE];
int head;
int rear;
};
void queue_init(struct Queue* q)
{
q->head = 0;
q->rear = 0;
}
int queue_is_full(struct Queue* q)
{
return (q->rear+1)%MAX_QUEUE==q->head;
}
int queue_enqueue(struct Queue* q, int e)
{
if(!queue_is_full(q))
{
q->data[q->rear] = e;
q->rear = (q->rear+1) % MAX_QUEUE;
return 0;
}else
{
return -1;
}
}
int queue_is_empty(struct Queue* q)
{
return q->head==q->rear;
}
int queue_dequeue(struct Queue* q, int* e)
{
if(!queue_is_empty(q))
{
*e = q->data[q->head];
q->head = (q->head+1) % MAX_QUEUE;
return 0;
}else
{
return -1;
}
}
void graph_visit(struct Graph* g, int i)
{
printf("Visit %d\n", g->vexs[i].data);
}
void graph_bfs(struct Graph* g)
{
int i, data;
int flags[MAX_VEXS];
struct Queue q;
struct Arc* ptr;
memset(flags, 0, sizeof(int)*MAX_VEXS);
queue_init(&q);
for(i=0; i<g->nvexs; i++)
{
if(!flags[i])
{
flags[i] = 1;
graph_visit(g, i);
queue_enqueue(&q, i);
while(!queue_is_empty(&q))
{
queue_dequeue(&q, &data);
ptr = g->vexs[data].first_arc;
while(ptr!=NULL)
{
if(!flags[ptr->ivex])
{
flags[ptr->ivex] = 1;
graph_visit(g, ptr->ivex);
queue_enqueue(&q, ptr->ivex);
}
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
struct Graph g;
graph_init(&g);
graph_create(&g);
//graph_print(&g);
graph_bfs(&g);
graph_free(&g);
return 0;
}
测试数据:
8 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 1 2 1 3 2 4 2 5 5 8 4 8 3 6 3 7 6 7