路径长度:从树中一个结点到另一个结点之间的分支构成这两个结点之间的路径,路径上的分支数目称作路径长度。
树的路径长度:从树根到每一个结点的路径长度之和。
结点的带全路径长度:从该结点到树根之间的路径长度与结点上权的乘积。
树的带全路径长度:树中所有叶子结点的带全路径长度之和,WPL = Σ (wi x li),其中wi是叶子结点的权重,li是从根到该叶子结点的路径长度,注意,带全路径长度只有叶子结点有权重!其他结点只计算长度无权重!。
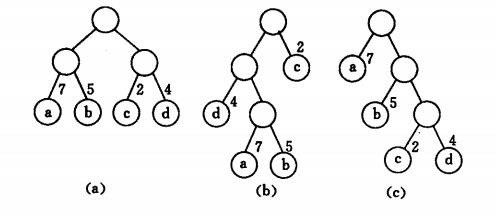
来看书上三个树的WPL:
WPL(a) = 7*2 + 5* 2 + 2*2 +4*2 = 36
WPL(b)=4*2 + 7*3 + 5*3 + 2 = 46
WPL(c) = 7 + 5 * 2 + 3 * 2 + 4 * 3 = 35
其实c是最优二叉树。
赫夫曼(Huffman)树,又称最优二叉树,是一类带全路径长度最短的树。
赫夫曼编码的用途很广,例如优化if分支条件的组合、数据压缩等等。
赫夫曼算法
设有n个叶子结点,则有对应的n个权值w1...wn。
(1)首先构成n棵二叉树,每棵二叉树中以wi为根结点,左右孩子均为空,设n棵二叉树位于集合F中。
(2)在F中选取两棵根结点权值最小的树做为左右子树,构造一棵新的二叉树,并设置根结点的权值为左、右子树上的根结点的权值之和。
(3)在F中删除这两棵被选中的子树,并且在F中加入新树。
(4)重复(2)和(3)直到F中只包含一棵树为止。
最后形成的这棵树便是赫夫曼树。
其实,赫夫曼算法的思想很简单:让权值大的尽量少在路径短的上面。权值小的在路径长的上面。
由于赫夫曼树中没有度为1的结点,所以一棵有n个叶子结点的赫夫曼树一定有2n-1个结点。
赫夫曼编码
在需要压缩编码的时候,可以另每种字符做为叶子结点,借助最优二叉树(赫夫曼树)设计长短不等的编码。
这种编码叫做前缀编码:长短不等的编码,且必须是任意一个字符的编码都不是另一个字符编码的前缀。
由于赫夫曼编码不仅需要左、右孩子,还需要双亲、还需要计算和合并。我们可以采用如下的结点数据结构:
struct HFNode
{
int weight;
int parent, lchild, rchild;
};
typedef struct HFNode[MAX] HFTree;
如上所述,weight是结点的权重。
赫夫曼树用数组存放,lchild和rchild是左右孩子在数组中的下标。
有了这个结构后,实现赫夫曼树的算法就比较简单了。
算法共分为三部分:
(1)构造赫夫曼树
(2)计算(打印)字符的赫夫曼编码
(3)利用赫夫曼编码译码
首先是构造赫夫曼树的编码,假设n个叶子结点(要编码的字符) ,我们用2*n-1个结点的数组存储赫夫曼树:
(a)[0, n-1]是n个叶子结点和weight,parent都是-1(未决定),lchild和rchild是0。
(b)[n, 2*n-1)是非叶子结点,我们从前面选择了min 2个结点后,组装的结点依次存放在n~2*n-1里面。
构造赫夫曼树的算法如下:
注意,算法中“直到只剩下一棵树” 这个条件,我们是可以通过控制for循环的次数控制(i->(n-1, 2*n-1)),而不用去判断的。
#include <stdio.h>
#define NODE 100
#define MAX 2*NODE-1
typedef struct HFNode
{
int weight;
int parent;
int lchild;
int rchild;
}HFNode, *HFTree;
void hftree_init(HFTree tree)
{
int i;
for(i=0;i<MAX;i++)
{
tree[i].weight = tree[i].lchild = tree[i].rchild = 0;
tree[i].parent = -1;
}
}
int hftree_min(HFTree tree, int start, int end)
{
int min = 0;
int minw = 0xffffff;
int i;
for(i=start; i<=end;i++)
{
if(tree[i].parent==-1 && tree[i].weight<minw)
{
minw = tree[i].weight;
min = i;
}
}
return min;
}
void hftree_build(HFTree tree, int* w, int nw)
{
int i, m;
int min1, min2;
// First , fill HFTree[0:n-1] with weight (leaf node)
for(i=0;i<nw;i++)
{
tree[i].weight = w[i];
tree[i].lchild = tree[i].rchild = 0; // leaf has no left or right child
tree[i].parent = -1; // parent undefined
}
// Second, build tree and set no-leaf node into HFTree[n: 2*n-1)
m = 2 * nw - 1;
for(i=nw;i<m;i++)
{
// Select two min and no parent node from [0:i-1]
min1 = hftree_min(tree, 0, i-1);
tree[min1].parent = i;
min2 = hftree_min(tree, 0, i-1);
tree[min2].parent = i;
// Make new node and store at i
tree[i].lchild = min1;
tree[i].rchild = min2;
tree[i].weight = tree[min1].weight + tree[min2].weight;
tree[i].parent = -1;
}
}
int main()
{
int i;
int w[8] = {5, 29, 7, 8, 14, 23, 3, 11};
int n = sizeof(w) / sizeof(int);
HFNode hftree[MAX];
// Init
hftree_init(hftree);
// Make tree
hftree_build(hftree, w, n);
// Print & Test
//for(i=0;i<2*n-1;i++)
//{
// printf("%2d %2d %2d %2d\n", hftree[i].weight, hftree[i].parent, hftree[i].lchild, hftree[i].rchild);
//}
hfcode_encode(hftree, w, n);
return 0;
}
然后是给每个字符(叶子结点) 赋予0/1编码,我们这里规定左子树0,右子树1:
void hfcode_encode(HFTree tree, int* w, int nw)
{
char tmp[1024];
int i, p, j;
// Get Huffman code each leaf to root
for(i=0;i<nw;i++)
{
j = 0;
p = i;
while(tree[p].parent!=-1)
{
if(tree[tree[p].parent].lchild==p)
{
tmp[j++] = '0';
} else if(tree[tree[p].parent].rchild==p)
{
tmp[j++] = '1';
}
p = tree[p].parent;
}
tmp[j] = 'void hfcode_encode(HFTree tree, int* w, int nw)
{
char tmp[1024];
int i, p, j;
// Get Huffman code each leaf to root
for(i=0;i<nw;i++)
{
j = 0;
p = i;
while(tree[p].parent!=-1)
{
if(tree[tree[p].parent].lchild==p)
{
tmp[j++] = '0';
} else if(tree[tree[p].parent].rchild==p)
{
tmp[j++] = '1';
}
p = tree[p].parent;
}
tmp[j] = '\0';
// Print huffman code
printf("%2d: %s\n", w[i], tmp);
}
}';
// Print huffman code
printf("%2d: %s\n", w[i], tmp);
}
}
最后的编码结果:
5: 1000 29: 01 7: 0111 8: 1111 14: 011 23: 10 3: 0000 11: 100